
This is the second paragraph written by. Let's look at an example where we set the overflow-y to visible.
#SCROLL ON OVERFLOW CSS HOW TO#
We will discuss the overflow-y property below, exploring examples of how to use this property in CSS. I want to limit the height of the body with the visible screen size of the browser. For example in the demo below the horizontal overflow can be scrolled through whilst the text that extends beyond the height of the box is hidden. It’s also possible to manipulate the overflow of content horizontally or vertically with the overflow-x and overflow-y properties. The scrollbars will only show up if there is content that actually breaks out of the element. Use overflow-x-scroll to allow horizontal scrolling and always show scrollbars unless always-visible scrollbars are disabled by the operating system. autoĪuto overflow is very similar to the scroll value, only it solves the problem of getting scrollbars when you don’t need them. Note: In OS X Lion, when scrollbars are set to only show when being used, scroll behaves more like auto, in that only needed scrollbars will show up.

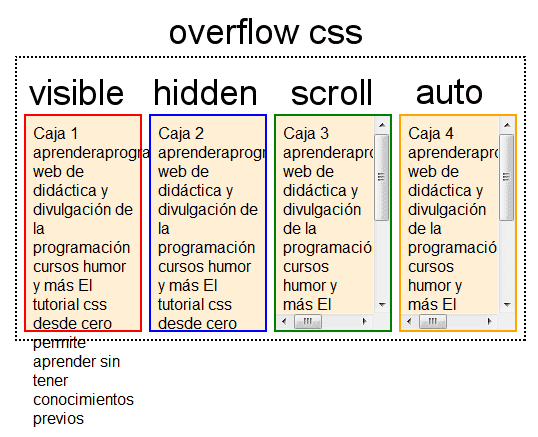
IOS’ momentum scrolling can be enabled for this value with -webkit-overflow-scrolling. Of note with this value is that you get BOTH horizontal and vertical scrollbars no matter what, even if the content requires only one or the other. Setting the overflow value of a box to scroll will hide the content from rendering outside the box, but will offer scrollbars to scroll the interior of the box to view the content. So for example a user has their default font size set larger than you would expect, you may be pushing text outside of a box and hiding it completely from their view. However, bear in mind that content that is hidden in this way is utterly inaccessible (short of viewing the source). This is particularly useful in use with dynamic content and the possibility of an overflow causing serious layout problems. This literally hides any content that extends beyond the box.

The opposite of the default visible is hidden. Generally, you shouldn’t be setting static heights on boxes with web text in them anyway, so it shouldn’t come up. The content renders outside the elements box 2. The overflowproperty has the following values: 1. The important thing to remember here is that even though the content is visible outside of the box, that content does not affect the flow of the page. The overflowproperty specifies whether to clip the content or to add scrollbars when the content of an element is too big to fit in the specified area. So in general, there is no reason to explicitly set this property to visible unless you are overriding it from being set elsewhere. If you don’t set the overflow property at all, the default is visible. Overflow comes into play more commonly when explicit widths and heights are set and it would be undesirable for any content to spill out, or when scrolling is explicitly being avoided. Unless a height is set, text will just push an element taller as well. Remember that text will naturally wrap at the end of an element (unless white-space is changed) so text will rarely be the cause of overflow. inherit: sets the overflow to the value of its parent element.initial: uses the default value which is visible.auto: if the content proceeds outside its box then that content will be hidden whilst a scroll bar should be visible for users to read the rest of the content.This can be used with overflow-clip-margin to set the clipped area. clip: content is clipped when it proceeds outside its box.scroll: similar to hidden except users will be able to scroll through the hidden content.

It applies to window objects, but also to scrollable frames and elements with the overflow CSS property set to. hidden: overflowing content will be hidden. scrolls to a different place in the element.This is the default value of the property visible: content is not clipped when it proceeds outside its box.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
